
The Bantu people represent a vast and diverse cultural group that has spread across much of Sub-Saharan Africa, encompassing a wide range of ethnicities, languages, and traditions. With a shared linguistic heritage and cultural roots, the Bantu people have woven a rich and intricate tapestry that continues to shape the continent’s identity.
From the savannas of East Africa to the forests of Central Africa, and from the deserts of Southern Africa to the coastlines of West Africa, the Bantu people have left an indelible mark on the African landscape. Their shared language, traditions, and social structures have created a common cultural currency that transcends national borders and ethnic divisions.
The Bantu people’s cultural heritage is a testament to their resilience, adaptability, and creativity. Their traditions, customs, and beliefs have been shaped by their history, geography, and interactions with other cultures. From the intricate wood carvings of the Makonde people to the vibrant textiles of the Kuba people, Bantu cultural expressions are a celebration of diversity, innovation, and community.
As a cultural force, the Bantu people continue to influence the continent’s identity, shaping its music, art, literature, and politics. Their legacy serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of cultural heritage, community, and resilience in the face of adversity.
Origins and Migrations
Origins
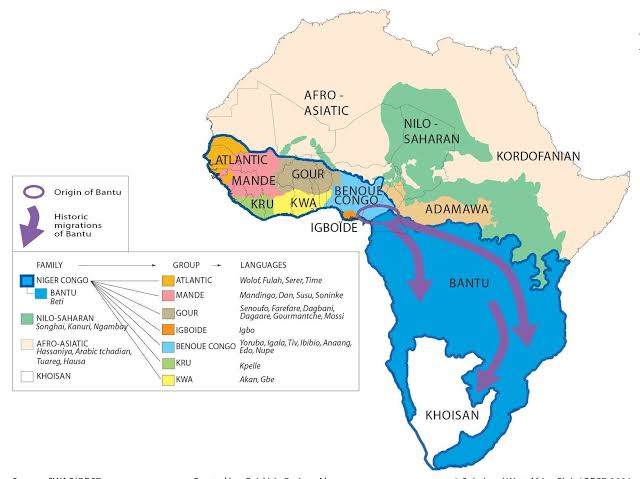
The Bantu people trace their origins to the region of present-day Cameroon and Nigeria, where they developed a shared Bantu language and cultural practices.
Migrations
Over several centuries, the Bantu people embarked on a massive expansion, spreading their language and customs throughout much of Central, Eastern, and Southern Africa
Influence
The Bantu migrations had a profound impact on the cultures and populations they encountered, leading to the widespread adoption of Bantu languages and traditions
Language and Dialects
Linguistic Diversity
The Bantu languages form a vast group of closely related languages, with over 500 distinct dialects spoken across the African continent
Common Roots
Despite this diversity, all Bantu languages share a common Bantu root, reflecting the shared origins and cultural heritage of the Bantu people.
Language Preservation
Efforts to preserve and promote Bantu languages have been crucial in maintaining the cultural identity and traditions of the Bantu people.
Social Structure and Traditions

Communal Living
Bantu communities traditionally centered around extended family groups, known as clans, that lived and worked together in close-knit villages.
Gender Roles
Bantu societies often had distinct gender roles, with men typically responsible for activities such as hunting and warfare, while women focused on agriculture and domestic tasks.
Rites of Passage
Bantu cultures place great importance on rituals and ceremonies that mark key life events, such as birth, coming-of-age, marriage, and death.
Oral Traditions
Storytelling, music, and dance are integral to Bantu cultural expression and the transmission of their rich history and values
Role of Kinship and Community Living


Family Bonds
Kinship and family ties are the foundation of Bantu social structure, with extended families living and working together in close-knit communities.
Communal Living
Bantu villages are organized around the principle of communal living, where resources, responsibilities, and decision-making are shared among all members of the community
Respect for Elders
Elders are highly revered in Bantu societies, with their wisdom and experience guiding the younger generations and the overall direction of the community.
Spiritual Beliefs and Practices
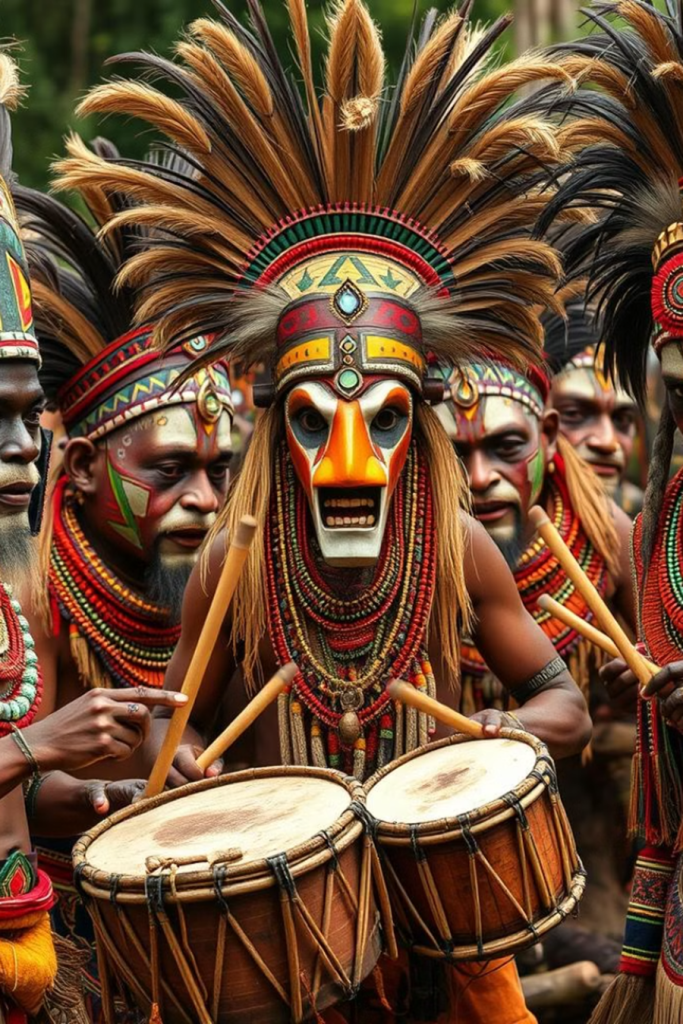

Ancestral Veneration
Bantu religions often involve the veneration of ancestors, who are believed to play an important role in the lives of the living.
Rituals and Ceremonies
Bantu spiritual practices are expressed through a rich tapestry of rituals, ceremonies, and traditional practices that connect the community to the divine.
Animistic Beliefs
Many Bantu belief systems are based on the idea that all things, including natural objects and phenomena, possess a spiritual essence or life force
Artistic Expressions and Craftsmanship
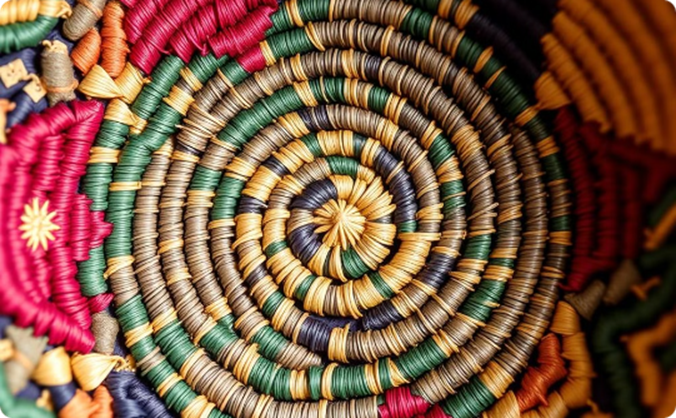

Weaving and Basketry
Bantu artisans are renowned for their exceptional weaving skills, creating intricate baskets, mats, and textiles that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
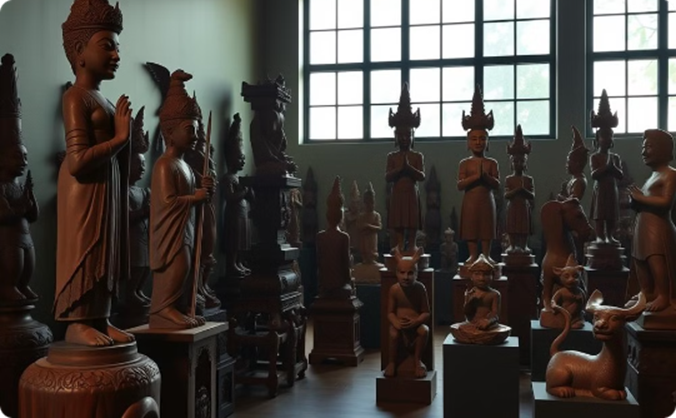

Woodcarving
Bantu woodcarvers are masters of their craft, producing exquisite sculptures, masks, and utilitarian objects that reflect their cultural heritage and spiritual beliefs.
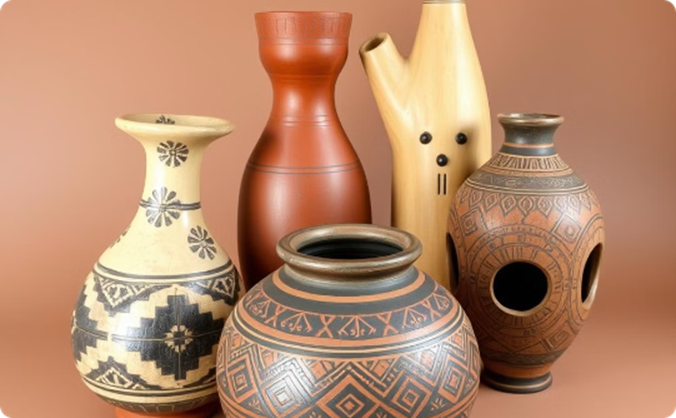

Pottery and Ceramics
Bantu potters create a wide range of ceramic vessels, from utilitarian storage jars to elaborate decorative pieces, using traditional techniques and designs.
The Bantu Diaspora: Legacy and Influence
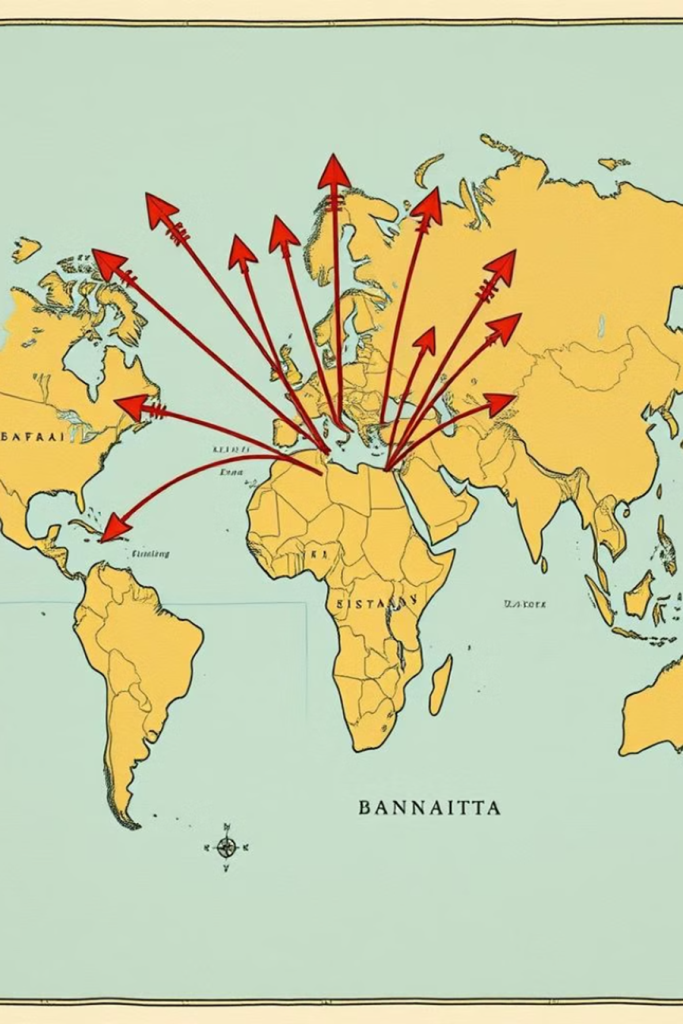
Dispersal
The Bantu migrations led to the spread of Bantu peoples and cultures throughout much of Africa, influencing the development of diverse societies and communities.
Transoceanic Connections
The Bantu diaspora also extended beyond Africa, as Bantu-speaking peoples were forcibly transported to the Americas and other parts of the world during the slave trade
Cultural Legacy
The Bantu cultural heritage continues to have a profound impact on the arts, music, languages, and traditions of many regions, both in Africa and the global African diaspora